Although the application of quenched rollers (usually referring to alloy steel or tool steel rollers treated by quenching process) in the aluminum foil industry is not as extreme as that of tungsten carbide guide rollers, it still has significant advantages in specific scenarios, especially suitable for cost sensitive or low to medium load production needs. The following are its core application advantages and applicable scenarios:
1. High surface hardness and wear resistance
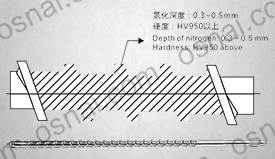
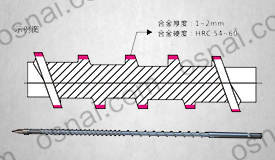
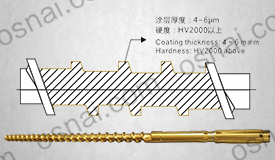
Advantages of quenching process: By quenching (such as high-frequency induction quenching, laser quenching, etc.), the hardness of the roller surface can reach HRC55-65, significantly improving wear resistance and withstanding friction and slight impact during aluminum foil rolling process.
Economic wear-resistant solution: Compared to tungsten carbide guide rollers, quenched rollers have lower initial costs and are suitable for low load production lines.
2. Good resistance to deformation
High rigidity structure: Quenched steel material has a high elastic modulus (about 200-210Gpa), with small deformation under rolling pressure, which can maintain the uniformity of aluminum foil thickness and reduce the risk of wrinkles and breakage.
Bending resistance: suitable for wide width aluminum foil rolling (such as width ≥ 1500mm), able to maintain good straightness even at larger roll body lengths,
3. Processing flexibility and repairability
Easy to process and repair: Hardened steel rollers can be surface repaired or size adjusted through conventional machining (such as grinding and turning), reducing maintenance costs; Once the tungsten carbide guide roller is worn or damaged, it is difficult and costly to repair.
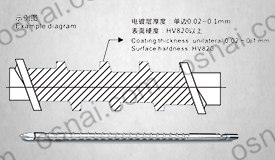
Surface modification potential: Corrosion resistance or friction performance can be further improved through surface treatments such as chrome plating and ceramic spraying, to meet different process requirements.
4. Impact toughness
Better toughness than hard alloy: The matrix material of quenched steel rollers (such as H13, D2 tool steel) has higher toughness, and in the event of accidental impact during aluminum foil rolling (such as aluminum foil strip breakage getting stuck in the roller gap), it is less likely to undergo brittle cracking, ensuring safety
5. Moderate temperature resistance
Stability at medium and low temperatures: Within the conventional temperature range of aluminum foil rolling (≤ 250 ° C), the thermal expansion coefficient of the quenched roll is relatively low, which can maintain dimensional stability; However, caution should be exercised during high-temperature annealing (>300 ℃) to avoid tempering softening.
Main application areas
1. Steel and metallurgical industry
Hot/cold rolling mill: capable of withstanding high pressure and high temperature, with quenched rollers ensuring uniform thickness and smooth surface of the sheet.
Continuous casting machine guide roller: guides high-temperature steel billets, wear-resistant and thermally deformed.
2. Mining and Building Materials
Crusher roller: crushes ore and cement raw materials, requiring extremely high wear resistance.
Roller drum: reduces surface damage when handling hard aggregates.
3. Paper making and printing
Polishing roller: improves the smoothness of the paper surface, and hardens the steel roller to avoid fiber wear.
Plate roller: Long term maintenance of printing pattern clarity.
4. Plastic and rubber processing
Rolling roller: Pressing plastic film or rubber sheet at high temperature, corrosion-resistant and anti stick.
Extruder roller: resistant to wear when handling filling materials such as fiberglass.
5. Other industrial sectors
Aluminum foil rolling: Ultra thin material processing requires extremely high roll surface precision.
Textile machinery: Pullers and rollers need to maintain a smooth surface for a long time.
|